Two-Phase Encryption
Two-Phase Encryption
Section titled “Two-Phase Encryption”Hyra Network implements a sophisticated two-phase encryption system that ensures maximum privacy and security for AI task processing. This system allows task data to be encrypted and securely transferred between AI end users, workers, and verifiers without compromising privacy.
Overview
Section titled “Overview”The two-phase encryption system consists of:
- Phase 1 - Task Submission: AI end user encrypts input data and wraps keys for verifier and user
- Phase 2 - Task Assignment: Verifier re-encrypts the AES key for the assigned worker
This approach ensures that:
- Only authorized parties can access the data
- Data remains encrypted throughout the entire process
- No single party has complete access to all data
- Privacy is maintained at all stages
Phase 1: Task Submission
Section titled “Phase 1: Task Submission”Step 1: Generate Random AES Key
Section titled “Step 1: Generate Random AES Key”# Example: Generate random AES keyfrom hyra_network.crypto import AESKeyGenerator
keygen = AESKeyGenerator()aes_key = keygen.generate_random_key(256) # 256-bit AES keyprint(f"Generated AES key: {aes_key.hex()}")// Example: Generate random AES keyconst { AESKeyGenerator } = require("@hyra-network/sdk");
const keygen = new AESKeyGenerator();const aesKey = keygen.generateRandomKey(256); // 256-bit AES keyconsole.log(`Generated AES key: ${aesKey.toString("hex")}`);Step 2: Encrypt Input Data
Section titled “Step 2: Encrypt Input Data”# Example: Encrypt input data with AES keyfrom hyra_network.crypto import AESEncryption
aes = AESEncryption()encrypted_data = aes.encrypt(input_data, aes_key)print(f"Encrypted data: {encrypted_data.hex()}")// Example: Encrypt input data with AES keyconst { AESEncryption } = require("@hyra-network/sdk");
const aes = new AESEncryption();const encryptedData = aes.encrypt(inputData, aesKey);console.log(`Encrypted data: ${encryptedData.toString("hex")}`);Step 3: Wrap AES Key for Verifier
Section titled “Step 3: Wrap AES Key for Verifier”# Example: Wrap AES key for verifierfrom hyra_network.crypto import AsymmetricEncryption
crypto = AsymmetricEncryption()verifier_wrapped_key = crypto.encrypt(aes_key, verifier_public_key)print(f"Verifier wrapped key: {verifier_wrapped_key.hex()}")// Example: Wrap AES key for verifierconst { AsymmetricEncryption } = require("@hyra-network/sdk");
const crypto = new AsymmetricEncryption();const verifierWrappedKey = crypto.encrypt(aesKey, verifierPublicKey);console.log(`Verifier wrapped key: ${verifierWrappedKey.toString("hex")}`);Step 4: Wrap AES Key for User
Section titled “Step 4: Wrap AES Key for User”# Example: Wrap AES key for useruser_wrapped_key = crypto.encrypt(aes_key, user_public_key)print(f"User wrapped key: {user_wrapped_key.hex()}")// Example: Wrap AES key for userconst userWrappedKey = crypto.encrypt(aesKey, userPublicKey);console.log(`User wrapped key: ${userWrappedKey.toString("hex")}`);Step 5: Submit to Smart Contract
Section titled “Step 5: Submit to Smart Contract”# Example: Submit encrypted task to smart contractfrom hyra_network.smart_contracts import TaskPool
task_pool = TaskPool()task_data = { 'encrypted_data': encrypted_data, 'verifier_wrapped_key': verifier_wrapped_key, 'user_wrapped_key': user_wrapped_key, 'worker_wrapped_key': None # Will be set in Phase 2}
tx_hash = task_pool.submit_task(task_data)print(f"Task submitted: {tx_hash}")// Example: Submit encrypted task to smart contractconst { TaskPool } = require("@hyra-network/sdk");
const taskPool = new TaskPool();const taskData = { encryptedData: encryptedData, verifierWrappedKey: verifierWrappedKey, userWrappedKey: userWrappedKey, workerWrappedKey: null, // Will be set in Phase 2};
const txHash = await taskPool.submitTask(taskData);console.log(`Task submitted: ${txHash}`);Phase 2: Task Assignment & Re-encryption
Section titled “Phase 2: Task Assignment & Re-encryption”Step 1: Worker Requests Task
Section titled “Step 1: Worker Requests Task”# Example: Worker requests taskfrom hyra_network.smart_contracts import TaskRouter
task_router = TaskRouter()task = task_router.get_task(worker_public_key)print(f"Task assigned: {task['task_id']}")// Example: Worker requests taskconst { TaskRouter } = require("@hyra-network/sdk");
const taskRouter = new TaskRouter();const task = await taskRouter.getTask(workerPublicKey);console.log(`Task assigned: ${task.taskId}`);Step 2: Verifier Re-encrypts AES Key
Section titled “Step 2: Verifier Re-encrypts AES Key”# Example: Verifier re-encrypts AES key for workerfrom hyra_network.crypto import VerifierEncryption
verifier_crypto = VerifierEncryption()
# Decrypt AES key with verifier's private keyaes_key = verifier_crypto.decrypt(verifier_wrapped_key, verifier_private_key)
# Re-encrypt AES key for worker's public keyworker_wrapped_key = verifier_crypto.encrypt(aes_key, worker_public_key)print(f"Worker wrapped key: {worker_wrapped_key.hex()}")// Example: Verifier re-encrypts AES key for workerconst { VerifierEncryption } = require("@hyra-network/sdk");
const verifierCrypto = new VerifierEncryption();
// Decrypt AES key with verifier's private keyconst aesKey = verifierCrypto.decrypt(verifierWrappedKey, verifierPrivateKey);
// Re-encrypt AES key for worker's public keyconst workerWrappedKey = verifierCrypto.encrypt(aesKey, workerPublicKey);console.log(`Worker wrapped key: ${workerWrappedKey.toString("hex")}`);Step 3: Update Smart Contract
Section titled “Step 3: Update Smart Contract”# Example: Update smart contract with worker wrapped keytask_pool.add_worker_key(task_id, worker_wrapped_key)print(f"Worker key added for task: {task_id}")// Example: Update smart contract with worker wrapped keyawait taskPool.addWorkerKey(taskId, workerWrappedKey);console.log(`Worker key added for task: ${taskId}`);Phase 3: Task Processing
Section titled “Phase 3: Task Processing”Step 1: Worker Gets Task Data
Section titled “Step 1: Worker Gets Task Data”# Example: Worker gets encrypted task datatask_data = task_pool.get_task_data(task_id)encrypted_data = task_data['encrypted_data']worker_wrapped_key = task_data['worker_wrapped_key']// Example: Worker gets encrypted task dataconst taskData = await taskPool.getTaskData(taskId);const encryptedData = taskData.encryptedData;const workerWrappedKey = taskData.workerWrappedKey;Step 2: Worker Decrypts Data
Section titled “Step 2: Worker Decrypts Data”# Example: Worker decrypts task datafrom hyra_network.crypto import WorkerDecryption
worker_crypto = WorkerDecryption()
# Decrypt AES key with worker's private keyaes_key = worker_crypto.decrypt(worker_wrapped_key, worker_private_key)
# Decrypt task data with AES keyplaintext_input = worker_crypto.decrypt(encrypted_data, aes_key)print(f"Decrypted input: {plaintext_input}")// Example: Worker decrypts task dataconst { WorkerDecryption } = require("@hyra-network/sdk");
const workerCrypto = new WorkerDecryption();
// Decrypt AES key with worker's private keyconst aesKey = workerCrypto.decrypt(workerWrappedKey, workerPrivateKey);
// Decrypt task data with AES keyconst plaintextInput = workerCrypto.decrypt(encryptedData, aesKey);console.log(`Decrypted input: ${plaintextInput}`);Step 3: Process AI Task
Section titled “Step 3: Process AI Task”# Example: Process AI taskfrom hyra_network.ai import AIProcessor
ai_processor = AIProcessor()result = ai_processor.process_task(plaintext_input, model_name)print(f"AI result: {result}")// Example: Process AI taskconst { AIProcessor } = require("@hyra-network/sdk");
const aiProcessor = new AIProcessor();const result = await aiProcessor.processTask(plaintextInput, modelName);console.log(`AI result: ${result}`);Phase 4: Output Encryption
Section titled “Phase 4: Output Encryption”Step 1: Generate New AES Key for Output
Section titled “Step 1: Generate New AES Key for Output”# Example: Generate new AES key for outputoutput_aes_key = keygen.generate_random_key(256)print(f"Output AES key: {output_aes_key.hex()}")// Example: Generate new AES key for outputconst outputAESKey = keygen.generateRandomKey(256);console.log(`Output AES key: ${outputAESKey.toString("hex")}`);Step 2: Encrypt Output Data
Section titled “Step 2: Encrypt Output Data”# Example: Encrypt output dataencrypted_output = aes.encrypt(result, output_aes_key)print(f"Encrypted output: {encrypted_output.hex()}")// Example: Encrypt output dataconst encryptedOutput = aes.encrypt(result, outputAESKey);console.log(`Encrypted output: ${encryptedOutput.toString("hex")}`);Step 3: Wrap Output AES Key for Multiple Recipients
Section titled “Step 3: Wrap Output AES Key for Multiple Recipients”# Example: Wrap output AES key for multiple recipientsoutput_wrapped_keys = { 'verifier': crypto.encrypt(output_aes_key, verifier_public_key), 'user': crypto.encrypt(output_aes_key, user_public_key), 'worker': crypto.encrypt(output_aes_key, worker_public_key)}
print(f"Output wrapped keys: {output_wrapped_keys}")// Example: Wrap output AES key for multiple recipientsconst outputWrappedKeys = { verifier: crypto.encrypt(outputAESKey, verifierPublicKey), user: crypto.encrypt(outputAESKey, userPublicKey), worker: crypto.encrypt(outputAESKey, workerPublicKey),};
console.log(`Output wrapped keys: ${outputWrappedKeys}`);Step 4: Submit Encrypted Result
Section titled “Step 4: Submit Encrypted Result”# Example: Submit encrypted resultresult_data = { 'encrypted_output': encrypted_output, 'wrapped_keys': output_wrapped_keys}
tx_hash = task_pool.submit_result(task_id, result_data)print(f"Result submitted: {tx_hash}")// Example: Submit encrypted resultconst resultData = { encryptedOutput: encryptedOutput, wrappedKeys: outputWrappedKeys,};
const txHash = await taskPool.submitResult(taskId, resultData);console.log(`Result submitted: ${txHash}`);Phase 5: Access Results
Section titled “Phase 5: Access Results”Step 1: User Gets Encrypted Result
Section titled “Step 1: User Gets Encrypted Result”# Example: User gets encrypted resultresult_data = task_pool.get_result(task_id)encrypted_output = result_data['encrypted_output']user_wrapped_key = result_data['wrapped_keys']['user']// Example: User gets encrypted resultconst resultData = await taskPool.getResult(taskId);const encryptedOutput = resultData.encryptedOutput;const userWrappedKey = resultData.wrappedKeys.user;Step 2: User Decrypts Result
Section titled “Step 2: User Decrypts Result”# Example: User decrypts resultfrom hyra_network.crypto import UserDecryption
user_crypto = UserDecryption()
# Decrypt AES key with user's private keyoutput_aes_key = user_crypto.decrypt(user_wrapped_key, user_private_key)
# Decrypt output data with AES keyplaintext_output = user_crypto.decrypt(encrypted_output, output_aes_key)print(f"Final result: {plaintext_output}")// Example: User decrypts resultconst { UserDecryption } = require("@hyra-network/sdk");
const userCrypto = new UserDecryption();
// Decrypt AES key with user's private keyconst outputAESKey = userCrypto.decrypt(userWrappedKey, userPrivateKey);
// Decrypt output data with AES keyconst plaintextOutput = userCrypto.decrypt(encryptedOutput, outputAESKey);console.log(`Final result: ${plaintextOutput}`);Complete Sequence Diagram
Section titled “Complete Sequence Diagram”The following diagram shows the complete two-phase encryption workflow:
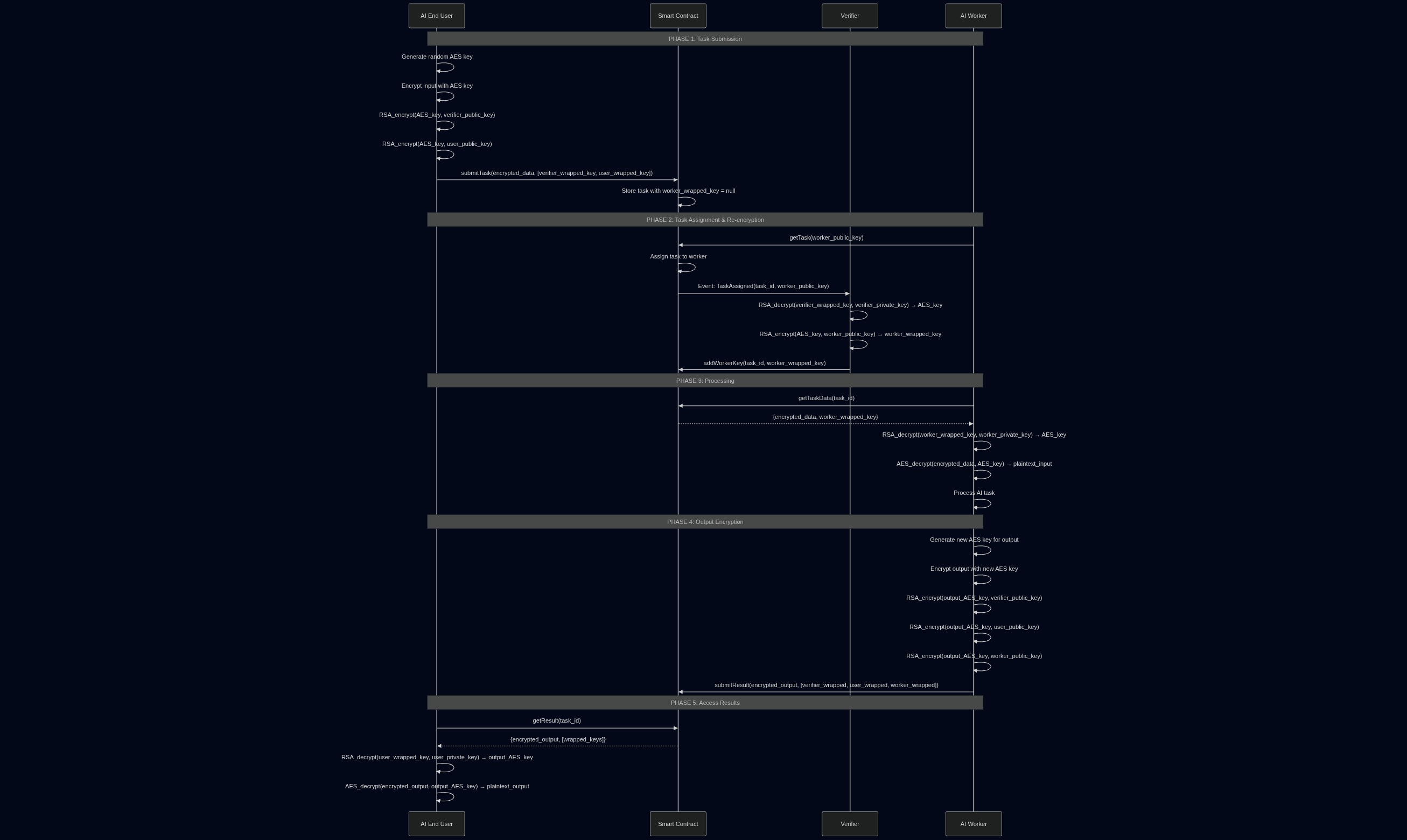
Phase 1: Task Submission
Section titled “Phase 1: Task Submission”- AI End User generates a random AES key
- AI End User encrypts input data with the AES key
- AI End User wraps the AES key for the verifier using RSA encryption
- AI End User wraps the AES key for themselves using RSA encryption
- AI End User submits the encrypted task to the smart contract
Phase 2: Task Assignment & Re-encryption
Section titled “Phase 2: Task Assignment & Re-encryption”- AI Worker requests a task from the smart contract
- Smart Contract assigns the task to the worker
- Smart Contract emits an event to notify the verifier
- Verifier decrypts the AES key using their private key
- Verifier re-encrypts the AES key for the worker’s public key
- Verifier adds the worker’s wrapped key to the smart contract
Phase 3: Processing
Section titled “Phase 3: Processing”- AI Worker gets the encrypted task data from the smart contract
- AI Worker decrypts the AES key using their private key
- AI Worker decrypts the task data using the AES key
- AI Worker processes the AI task
Phase 4: Output Encryption
Section titled “Phase 4: Output Encryption”- AI Worker generates a new AES key for the output
- AI Worker encrypts the output with the new AES key
- AI Worker wraps the output AES key for the verifier
- AI Worker wraps the output AES key for the user
- AI Worker wraps the output AES key for themselves
- AI Worker submits the encrypted result to the smart contract
Phase 5: Access Results
Section titled “Phase 5: Access Results”- AI End User gets the encrypted result from the smart contract
- AI End User decrypts the output AES key using their private key
- AI End User decrypts the output data using the AES key
- AI End User receives the final AI result
Security Benefits
Section titled “Security Benefits”1. Maximum Privacy
Section titled “1. Maximum Privacy”- No single party has access to all data
- Data remains encrypted throughout the entire process
- Only authorized parties can decrypt specific parts
2. Flexible Access Control
Section titled “2. Flexible Access Control”- Verifier can decrypt input data for verification
- Worker can decrypt input data for processing
- User can decrypt output data for results
- Multiple parties can access output data as needed
3. Audit Trail
Section titled “3. Audit Trail”- All operations are recorded on blockchain
- Encryption keys are tracked and managed
- Access patterns are visible and verifiable
Implementation Considerations
Section titled “Implementation Considerations”1. Key Management
Section titled “1. Key Management”- Secure key storage for all parties
- Key rotation for enhanced security
- Backup and recovery procedures
2. Performance Optimization
Section titled “2. Performance Optimization”- Batch operations for multiple tasks
- Caching for frequently accessed data
- Hardware acceleration for encryption operations
3. Error Handling
Section titled “3. Error Handling”- Graceful degradation for failed operations
- Retry mechanisms for network issues
- Fallback procedures for key recovery
Best Practices
Section titled “Best Practices”1. Key Security
Section titled “1. Key Security”- Use strong random keys for AES encryption
- Protect private keys with secure storage
- Rotate keys regularly for enhanced security
2. Data Handling
Section titled “2. Data Handling”- Validate all inputs before encryption
- Use authenticated encryption for data integrity
- Implement proper error handling
3. Network Security
Section titled “3. Network Security”- Use secure communication channels
- Implement proper authentication for all parties
- Monitor for suspicious activity
Resources
Section titled “Resources”- Two-Phase Encryption Documentation: docs.hyra.network/two-phase-encryption
- Security Best Practices: docs.hyra.network/security
- GitHub: github.com/hyra-network
- Discord: discord.gg/hyra
Next Steps
Section titled “Next Steps”Ready to implement two-phase encryption? Check out our guides:
- Encryption - Learn about our encryption mechanisms
- Getting Started - Set up your development environment
- SDKs - Use our development tools
